channel 介绍
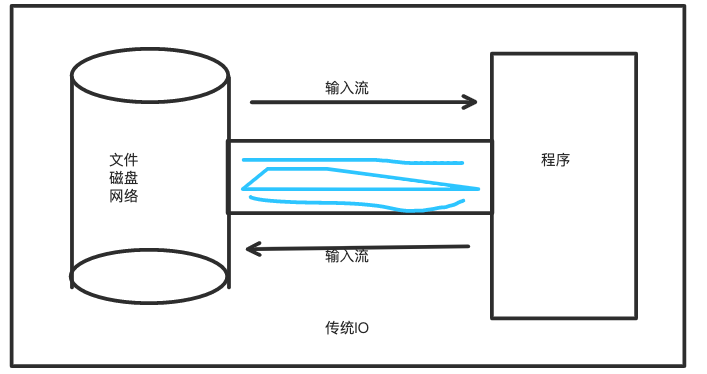
通道(channel) :由java.nio.channels包定义的,channel 表示IO源与目标打开的连接 。
Channel 类似于传统的流,只不过channel 本身不能直接访问数据,channel 只能与buffer进行交互
一、通道(channel)
用于源节点与目标节点的连接,在java nio中负责缓冲区数据的传输。channel本身不存储数据,因此需要配合缓冲区进行传输。
- 流与通道的区别
1、流是单向的,通道是双向的,可读可写。
2、流读写是阻塞的,通道可以异步读写。
3、流中的数据可以选择性的先读到缓存中,通道的数据总是要先读到一个缓存中,或从缓 存中写入
二、通道的主要实现类
Java.nio.channels.Channel接口
|–FileChannel
|–SocketChannel
|–ServerSocetChannel
|–DataramChannel
三、获取通道
JAVA针对支持通道的类提供了getChannel()方法
本地IO
FileInputStream/FileOutputStream
RamdomAccessFile
网络IO
Socket
ServerSocket
DatagramSocket
在JDK1.7中的NIO.2 针对各个通道提供了静态方法open()
在JDK1.7中的Files工具类的newByteChannel()
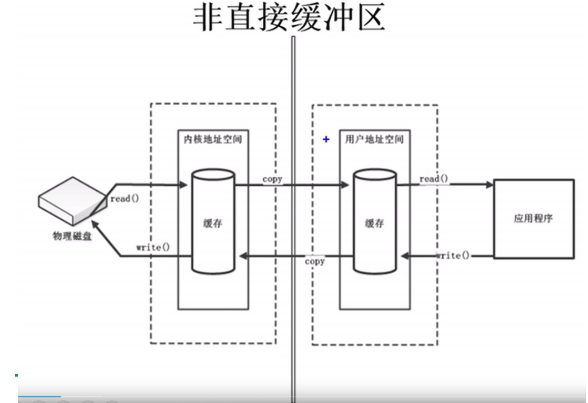
四、非直接缓冲区使用channel的dome
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
| public static void main(String[] args) {
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
//nio 文件复制
try {
fis = new FileInputStream("C:\\Users\\12113\\Desktop\\1.html");
fos = new FileOutputStream("C:\\Users\\12113\\Desktop\\nio.html");
FileChannel fosChannel = fos.getChannel();
FileChannel fisChannel = fis.getChannel();
ByteBuffer buffer =ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
while (fisChannel.read(buffer)!=-1){
buffer.flip(); //写模式
fosChannel.write(buffer);
buffer.clear();
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
|
五、直接缓冲区使用channel
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileChannel fileInChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("C:\\Users\\12113\\Desktop\\temp.txt"), StandardOpenOption.READ);
FileChannel fileOutChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("C:\\Users\\12113\\Desktop\\nio3.txt"), StandardOpenOption.WRITE, StandardOpenOption.READ, StandardOpenOption.CREATE_NEW);
MappedByteBuffer inByteBuffer = fileInChannel.map(MapMode.READ_ONLY, 0, fileInChannel.size());
MappedByteBuffer outByteBuffer = fileOutChannel.map(MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0, fileInChannel.size());
byte[] dest =new byte[inByteBuffer.limit()];
inByteBuffer.get(dest);
outByteBuffer.put(dest);
}
//通道之间传输
fileInChannel.transferTo(0,fileInChannel.size(),fileOutChannel);
}
|
六、channel 的数据传输
transferTo()
transferFrom()
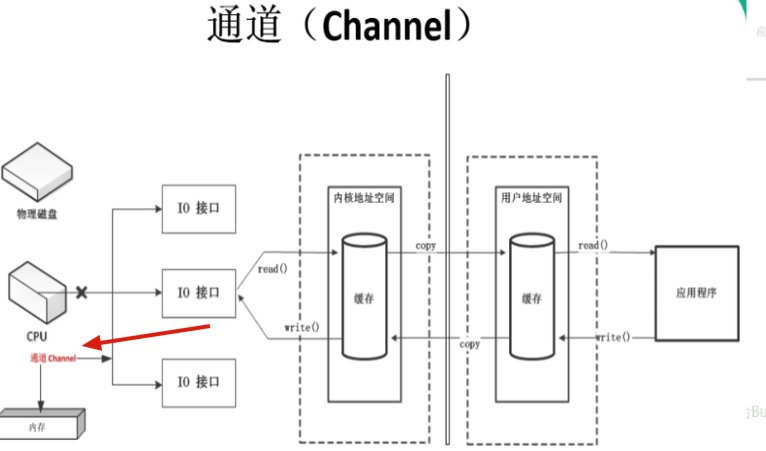
七、图解channel
Channel是一个独立的处理器,专门用于IO操作,附属于CPU。
在提出IO请求的时候,CPU不需要进行干预,也就提高了效率。